- shows amount of Real GDP that the private, public, and foreign sector collectively desire to purchase at each possible price level
- relationship between price level and level of Real GDP is inverse
- Price Level ↑ Real GDP ↓
- Price Level ↓ Real GDP ↑
- Aggregate Demand Curve
3 Reasons AD is Downward Sloping -
- Real-Balance Effect
- when price level is high, households and businesses cannot afford to purchase as much output
- when the price level is low, households and businesses can afford to purchase more output
- Interest-Rate Effect
- higher price level increases interest rates which tends to discourage investment
- lower price levels decrease interest rate which tends to encourage investment
- Foreign Purchases Effect
- higher price level increases demand for relatively cheaper imports
- lower price level increases foreign demand for relatively cheaper U.S. exports
Shifts in AD -
- 2 parts to shift in AD
- changes in C, Ig, G, and/or Xn
- multiplier effect that produces greater change than original change in the four components
- increase in AD = AD →
- decrease in AD = AD ←
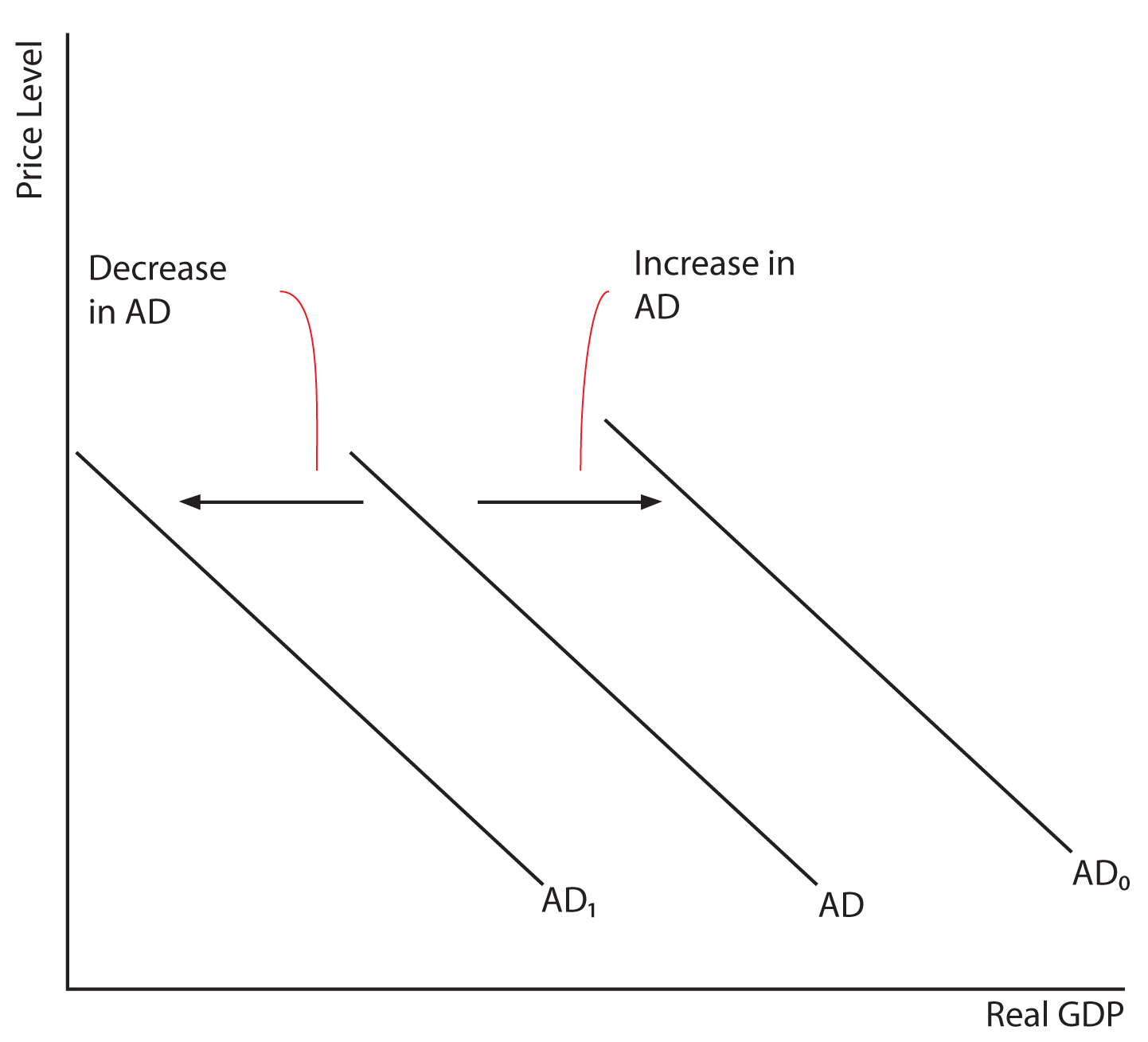
Shows the Decrease and Increase of AD
Consumption -
- Household spending is affect by :
- Consumer Wealth
- more wealth = more spending (AD →)
- less wealth = less spending (AD ←)
- Consumer Expectations
- positive expectations = more spending (AD →)
- ex : you know you will get a raise, so you go out and spend money the day before
- negative expectations = less spending (AD ←)
- Household Indebtedness
- less debt = more spending (AD →)
- more debt = less spending (AD ←)
- Taxes
- less taxes = more spending (AD →)
- more taxes = less spending (AD ←)
Gross Private Investment -
- Investment Spending is Sensitive to :
- Real Interest Rate
- lower real interest rate = more investment (AD →)
- higher real interest rate = less investment (AD ←)
- Expected Returns
- higher expected returns = more investment (AD →)
- lower expected returns = less investment (AD ←)
- expected returns are influenced by...
- expectations of future profitability
- technology
- degree of excess capacity (Existing Stock of Capital)
Government Spending -
- more government spending (AD →)
- less government spending (AD ←)
Net Exports -
- Net Exports are Sensitive to :
- Exchange Rates (international value of the dollar)
- strong dollar = more imports and fewer exports (AD →)
- weak dollar = less imports and more exports (AD →)
- Relative Income
- strong foreign economies = more exports (AD →)
- weak foreign economics = less exports (AD ←)
No comments:
Post a Comment