- new plants (factories)
- capital equipment (machinery)
- technology (hardware or software)
- new homes
- inventories (goods sold by producers)
Expected Rates of Return
- How do business make investment decisions?
- Cost / Benefit Analysis
- How does business determine benefits?
- Expected rate of return
- How does business cont cost?
- Interest costs
- How does business determine the amount of investment they undertake?
- compare expected rate of return to interest cost
- if expected rate of return is more than interest cost, then invest
- if expected rate of return is less than interest cost, DO NOT invest
Real GDP (r %) versus Nominal GDP (i %)
- Difference between the two :
- Nominal GDP - observable rate of interest rate subtracted out of inflation ( %)and is only known as an ex post facto
- How to compute real interest rate (r %)?
- r % = i % - %
- What determines the cost of an investment decision?
- real interest rate (r %)
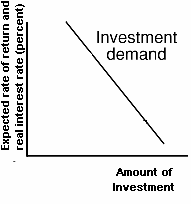
Investment Demand Curve (ID)
- What is the shape of the investment demand curve?
- downward sloping
- Why?
- when interest rates are high, fewer investments are profitable
- when interest rates are low, more investments are profitable
- ex :
Shifts in ID
- Cost of Production
- lower costs shift ID →
- higher costs shift ID ←
- Business Taxes
- lower business taxes (ID →)
- higher business taxes (ID ←)
- Technological Change
- new technology (ID →)
- lack of technology change (ID ←)
- Stock of Capital
- if an economy is low on capital, then ID →
- if an economy is much capital, then ID ←
- Expectations
- positive expectations (ID →)
- negative expectations (ID ←)

- Investment Demand shifts when different levels of Ig occur, even when r % is constant
No comments:
Post a Comment