- level of real GDP (GDPR or output)that firms will produce at each price level (PL)
Long Run -
- period of time where input prices are completely flexible and adjust to changes in price level
- the level of GDPR supplied is independent of price level
Short Run -
- period of time where input prices are sticky and do not adjust to changes in the price level
- level of GDPR supplied is directly related to the price level
Long Run Aggregare Supply (LRAS) -
- LRAS marks the level of full employment (FE) in the economy (analogous to PPC)
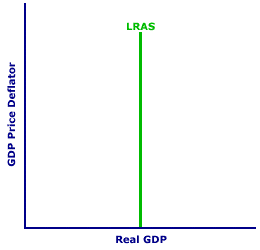
- Because of the input prices are completely flexible in the long run, changes in the pricelevel do not change the firms' real profits and therefore do not change the firms' level of output
- this means that the LRAS is vertical at an economy's level of full employment (FE or YF)
Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) -
- because input prices are sticky in SRAS, SRAS is upward sloping

Changes in the SRAS -
- increase in SRAS is seen as a shift to the right (SRAS )
- decrease in SRAS is ssseen as a shift to the left (SRAS )
- the key to understanding shifts in SRAS is per unit cost of production
- per-unit production cost = total input cost / total output

Shows the Decrease and Increase of SRAS
Determinants of SRAS (all affect unit production cost)
- Input Prices -
- Domestic Resource Prices
- wages (75% of all business costs)
- cost of capital
- raw materials (commodity prices)
- Foreign Resource Prices
- strong dollar = lower foreign resource prices
- weak dollar = higher foreign resource prices
- Market Power
- monopolies and cartels that control resources, control price of those resources
- increase in resource prices = SRAS ←
- decrease in resource prices = SRAS →
- Productivity -
- productivity = total output / total input
- more productivity = lower unit production cost (SRAS →)
- lower productivity = higher unit production cost (SRAS ←)
- Legal - Institutional Environment -
- Taxes and Subsidies -
- taxes (money that go to the government) on businesses, increase per unit production cost (SRAS ←)
- subsidies (money given from the government) to businesses, reduce per unit production cost (SRAS →)
- Government Regulation -
- government regulation creates a cost of compliance = SRAS ←
- deregulation reduces compliance costs = SRAS →
No comments:
Post a Comment